6 cybersecurity threats that are overlooked by businesses
The cybersecurity threat landscape is constantly evolving, and attacks are becoming more complex. In the past 12 months ransomware attacks have increased 64% year on year between August 2020 and August 2021. No business is completely immune to falling victim to a ransomware attack, however thankfully many businesses are investing time and money to protect their systems and networks to reduce this risk. A large component of a strong security posture is ensuring that employees and businesses are aware of cybersecurity threats, and most will be aware of the some of the common threats, however there are many other threats that businesses may be unaware of. In this article we will discuss 6 cybersecurity threats that are commonly overlooked by businesses.
Shadow IT
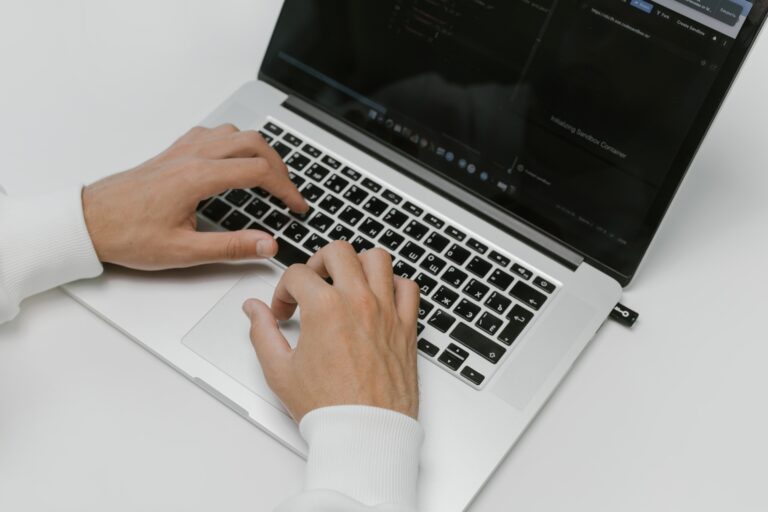
Shadow IT is the use of IT hardware or software used by a department or individual without the knowledge of the IT department or IT/security provider. This software may include cloud services or applications that departments use to increase productivity or to solve shortcomings of the provided software. The risk of using unauthorised software is that it may have a vulnerability that could lead to an attack on a business’s network or systems. Similarly, if employees use unauthorised file sharing platforms, it makes it possible for customer data to be vulnerable to a data breach. An example of shadow IT hardware may include employees using personal laptops or smartphones to access company data or networks. The risk of introducing this hardware to a company network is that it may be infected with malware that could spread to other devices on the network.
USB Drop Attacks
USB drop attacks are attacks whereby the cybercriminal leaves a USB infected with malware outside a business’s office space or in a carpark. An employee then picks up the USB and plugs it into a work device in an attempt to find the owner, but at this point it is too late and the device is infected with malware. This attack method has been the cause of many large-scale cyberattacks. Thankfully, it can easily be avoided through educating employees about the risk of inserting unknown devices into work computers.
Social Media Phishing
Phishing attacks are some of the most common attacks and have been for many years. These are social engineering attacks where an attacker sends a fraudulent message designed to trick an employee into revealing sensitive information or clicking on a malicious link. Typically, these attacks are through email, and many employees are wary of this and think twice before opening an email from an unknown sender. However, these attacks also take place on social media, where employees are less likely to consider the consequences of opening a link from someone on LinkedIn. Employees should treat messages on social media, or SMS messages with the same level of scrutiny they do for emails.
Insider Threats
An insider threat is an individual with legitimate access to company systems and data, that use that access, either maliciously or unintentionally, to cause harm to the organisation. This may include employees that are manipulated into performing malicious activities, such as downloading malware or giving away login credentials. These attacks also include employees or ex-employees that purposely infect a computer with malware or sell company data. A key method of preventing insider threats is to follow the principle of least privilege access, ensuring that employees are only able to access the data required to do their job, and nothing more.
IoT
Any device that has access to an organisations network or internet is vulnerable to being exploiting and used to spread ransomware throughout a business. This includes internet of things (IoT) devices. These are any devices that are connected to the internet and may include heating and cooling systems, smart speakers, TVs, CCTV systems or even smart coffee makers. Although all these items make benefit an organisation, they are at risk of being the entry point for a hacker. Businesses should be cautious about using these devices in an office space, and at the very least the devices should be on a separate network to other business devices, such as computers and servers.
Malvertising
Malvertising is a method of spreading malware using legitimate advertising space on websites. Cybercriminals pay for the advertising space and embed a small piece of malicious code within the advert that once clicked will direct the user to a compromised or malicious website. This will infect the victim’s device with malware that can then spread through a network leading to a widespread malware or ransomware attack. Due to the nature of this attack, the best way to avoid falling victim is to keep all browser up to date and avoid clicking on advertisements.
These are some of the cybersecurity threats that are commonly overlooked by businesses. Each year there are more threats that businesses face, and it can be difficult to stay up to date with the everchanging cybersecurity best practices.
If you want to keep your business secure with a comprehensive cybersecurity solution, get in touch with us today.